
Quantum Computing and the Financial System: A Future Outlook
Introduction: A Transformative Technology on the Horizon
Quantum computing remains in its early experimental phase, but its long-term potential to transform the financial system is undeniable. While practical, large-scale quantum computers are not yet available, research and development in this field are progressing rapidly. In the coming years and decades, quantum technology could significantly enhance financial modeling, risk assessment, and market efficiency, while also introducing new challenges in cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and systemic stability.
As financial institutions, central banks, and fintech innovators explore possible applications, it is becoming increasingly clear that quantum computing will not be just another technological upgrade—it will fundamentally change how financial markets operate. The question is not if quantum computing will impact finance but rather when and how institutions should prepare.
This article explores the potential real-world applications of quantum computing in the financial system, analyzing both opportunities and risks, and offering a long-term perspective on what financial institutions should consider today.
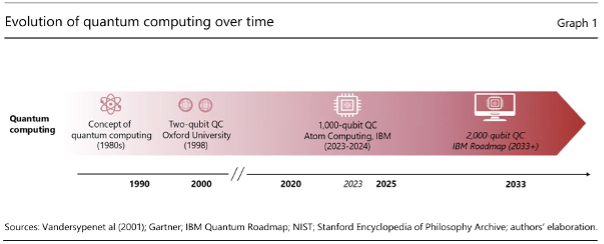
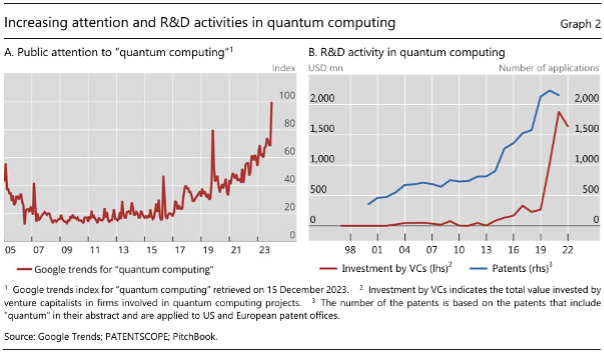
📖 Ref: BIS, 2024. Quantum computing and the financial system: opportunities and risks. https://www.bis.org/publ/bppdf/bispap149.pdf
📌 The Quantum Leap: How It Could Reshape the Financial System
1. Accelerating Risk Analysis and Financial Modeling
The financial system relies heavily on complex mathematical models to assess risk, forecast economic trends, and optimize investment strategies. Many of these models—such as Monte Carlo simulations, Black-Scholes pricing models, and stress-testing frameworks—require vast amounts of computational power.
Classical computers, even high-performance ones, struggle with these calculations as the complexity grows. Quantum computing, however, has the potential to make these processes exponentially more efficient by leveraging quantum algorithms that can process multiple variables simultaneously.
Potential Benefits:
- Faster and More Accurate Stress Testing: Financial institutions conduct stress tests to assess their resilience to economic shocks. Quantum computing could simulate thousands of economic conditions simultaneously, improving financial stability analysis.
- Portfolio Optimization at an Unprecedented Scale: Quantum algorithms could analyze millions of asset correlations, market conditions, and risk factors in real time, allowing investment firms to construct more optimal portfolios.
- Systemic Risk Identification: Quantum-enhanced models could identify hidden interdependencies in financial networks, helping regulators and central banks anticipate crises before they materialize.
While these applications remain theoretical at this stage, early research suggests that financial modeling will be one of the first areas where quantum computing delivers tangible value.
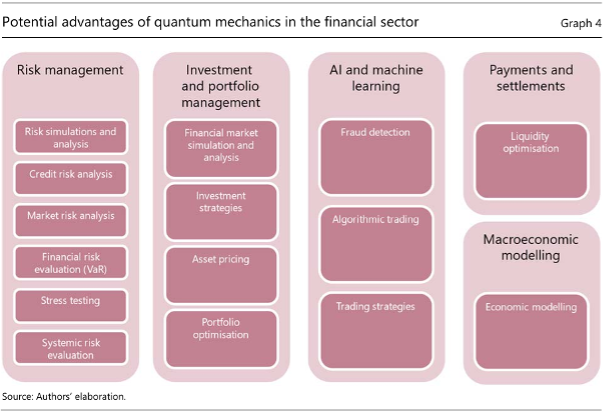
2. Quantum Optimization in Trading and Asset Pricing
One of the key advantages of quantum computing lies in optimization problems—a fundamental challenge in trading strategies, derivatives pricing, and market-making. Traditional optimization models rely on heuristic approaches that approximate the best outcomes but often fall short in highly complex financial environments.
Quantum optimization, however, could help solve these challenges with greater efficiency.
Potential Applications:
- Derivatives Pricing and Hedging Strategies: Quantum computers could process multi-asset derivatives pricing models in ways that classical computers cannot, helping financial institutions better hedge against volatility.
- Market Liquidity Optimization: Traders could use quantum algorithms to predict liquidity fluctuations, improving execution strategies for large transactions.
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT): Quantum computing could enhance HFT strategies by analyzing microsecond-level market patterns more efficiently than classical AI-driven models.
While quantum computing will not replace classical trading algorithms anytime soon, it could augment existing machine learning models, allowing market participants to achieve better price discovery and risk-adjusted returns.
3. The Future of Cryptography and Financial Security
Perhaps the most immediate concern for financial institutions is the threat quantum computing poses to encryption and cybersecurity. Most of the financial system’s security infrastructure—ranging from digital payments and interbank settlements to customer authentication and secure communications—relies on cryptographic protocols that are considered secure under classical computing constraints.
However, quantum computers could eventually break many of these encryption standards, leading to:
- Compromised financial transactions and the potential for widespread fraud.
- Exposure of confidential banking data, violating regulations like GDPR and PSD2.
- Threats to central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) and digital payment networks.
To mitigate this risk, researchers and central banks are already exploring post-quantum cryptography (PQC)—new cryptographic standards designed to withstand quantum attacks.
Key Developments in Quantum-Resistant Security:
- The NIST Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization Project is developing encryption algorithms that will remain secure even in a quantum computing era.
- Project Leap (BIS Innovation Hub) is testing quantum-safe cryptographic solutions for financial infrastructures, payment systems, and central banking networks.
- Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) offers a potential solution for ultra-secure financial transactions by leveraging quantum mechanics to detect interception attempts in real time.
Financial institutions should begin assessing their encryption frameworks now, as regulators will likely mandate a transition to quantum-resilient security protocols in the coming years.
4. Quantum Computing and Central Banking: Policy and Stability Considerations
While much of the focus on quantum computing in finance is centered on the private sector, central banks and financial regulators also have a vested interest in understanding how this technology could impact monetary policy, financial stability, and systemic risk management.
Quantum computing could enable central banks to:
- Model macroeconomic scenarios with greater accuracy, improving monetary policy decision-making.
- Enhance financial surveillance systems by detecting anomalous market activity in real time.
- Optimize cross-border payment infrastructures, making international settlements faster and more efficient.
However, quantum computing could also introduce regulatory challenges, such as:
- Potential market distortions if only a few firms gain early access to quantum-powered trading strategies.
- A new cybersecurity arms race, requiring regulators to enforce quantum-safe encryption across financial networks.
- The need for new compliance frameworks to ensure quantum-driven financial models remain transparent and auditable.
Central banks are already beginning to explore these issues, but international coordination will be crucial to ensuring a smooth transition into the quantum era.

🎯 Preparing for the Quantum Future: What Should Financial Institutions Do Today?
Although large-scale quantum computing is still years away, financial institutions should begin preparing for its eventual impact by:
- ✅ Monitoring Quantum Developments
- Keep track of advancements in quantum algorithms for finance.
- Engage with central banks and research institutions on quantum risk assessments.
- Stay informed on post-quantum cryptography standards and regulatory updates.
- ✅ Conducting a Quantum-Readiness Assessment
- Identify encryption vulnerabilities and assess exposure to potential quantum threats.
- Map out high-risk financial processes that could benefit from quantum-computing-enhanced modeling.
- Develop a long-term strategy for integrating quantum-powered risk management tools.
- ✅ Collaborating with Quantum Research Initiatives
- Participate in industry-wide discussions on quantum security and financial applications.
- Explore early-stage quantum fintech partnerships to test potential proofs of concept.
- Engage with regulatory bodies on shaping future compliance frameworks.

🚨 Conclusion: A Long-Term Transformation, Not an Immediate Disruption
Quantum computing is not an immediate disruptor, but its potential to reshape financial modeling, risk assessment, cryptography, and market operations makes it a critical area for long-term strategic planning.
Financial institutions that proactively engage with quantum research, monitor cybersecurity developments, and prepare for regulatory shifts will be better positioned to adapt to the coming changes.
While the timeline remains uncertain, one thing is clear: quantum computing will redefine the financial system in ways we are only beginning to understand.
🔍 Want to explore how quantum computing might impact your financial strategy?
🔗 Contact Studio AM for insights on quantum risk assessments and regulatory preparedness.



